Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease of the spine. It develops with age and consists of degenerative-dystrophic changes occurring in the intervertebral discs. For a long time there were no symptoms. A person may only notice some stiffness in the spine.
Osteochondrosis progresses slowly - many factors affect the rate of the disease. If the pathology is not treated, complications arise - sciatica, sciatica and others, depending on the spine. Some doctors believe that such a disease as osteochondrosis does not exist, and only those who do not understand human physiology make such a diagnosis.
causes
In the 21st century, the disease, compared to the 20th century, has noticeably rejuvenated. Very often you can meet young people who have degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs during a medical examination for another pathology. There is only one reason for this: urbanization and progress.
Today, a person does not need to make an effort to get to work or to eat. Most lead a sedentary lifestyle, eat malnourished and quickly gain weight, walk in the fresh air and active activities prefer a computer and a comfortable sofa. Even before work, many get into their own car, which is in the underground garage on the territory of a multi-storey building, and sit in the workplace for 7-9 hours or more.
On a note. Osteochondrosis is a human disease only. None of the mammals had such a pathology. You must understand that this is Homo sapiens' retribution for walking upright.
What causes osteochondrosis?
The following factors can lead to the appearance of the disease in the context of physical inactivity, lack of sufficient physical activity and an unhealthy lifestyle:
- violation of the metabolism of minerals and vitamins;
- a large number of transferred infectious diseases;
- chronic stress, depression;
- sudden movements, heavy lifting;
- Spinal injury;
- severe hypothermia;
- slouched;
- unnoticed over time and unhealed curvature of the spine;
- prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position (not necessarily sitting).
On a note. Major sports have a negative impact on human health. For example, weightlifting (and not only) in the future can become a trigger for degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs.

What happens to the spine?
The following factors directly affect back health:
- blood circulation in the paravertebral tissues is disturbed, the intervertebral discs suffer from a lack of nutrients (they do not have their own blood vessels and depend on the tissues around them);
- the muscular corset that supports the spine weakens, the vertebrae receive an additional load that they cannot bear;
- intervertebral discs lose moisture, decrease in volume and diameter - the spine seems to sag (many people notice that they become 5 or even 10 centimeters lower with age);
- there is instability of one or more parts of the spine;
- the body solves the problem of instability by developing osteophytes - these are marginal bony growths that over time tightly cement the spine, depriving it of flexibility.
On a note. The transformation of the spine itself does not cause pain - the pain syndrome appears when nerve roots, large arteries and lymphatic vessels are violated by osteophytes or the anatomical position of the vertebral bodies has changed.
Symptoms
Signs of osteochondrosis increase with the progression of the disease. There are 4 stages of pathology:
- First. Symptoms are completely absent. No pain. A person may experience a little more fatigue than usual, some stiffness in the spine, which is due to fatigue, excessive physical exertion and overwork. Osteochondrosis in the first stage can be
- Second. A persistent pain syndrome appears due to a violation of the nerve roots, which is easily stopped by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. If the patient continues to ignore the signals from his body and does not go to the doctor, the disease progresses rapidly. The flexibility of the spine is reduced, especially in the cervical and lumbar regions. The occurrence of vertebral artery syndrome is probably due to its compression either by edematous paravertebral tissues or by a displaced vertebra.
- Third. Pathology in poor condition. Pain haunts a person around the clock, weakening slightly in a horizontal position, but it is impossible to stay in one position for a long time (on your back, on your side). Sleep is disturbed, the patient becomes irritable. A person bends over (thoracic, lumbar), trying for a more comfortable position that would not cause discomfort, which becomes an impetus for the formation of a humpback, scoliosis and other spinal deformities.
- Fourth. There is an accretion of osteophytes - stabilization of the spine. The patient can look around only by turning the torso completely. The pain is strong, constant, completely eliminated only by blockages (novocaine, prednisolone). Disability in the fourth stage is about 80%.
Simultaneously with the listed signs, the patient may be tormented by symptoms that, at first glance, have nothing to do with the back - dizziness, flies in the eyes, high blood pressure, numbness of the upper limbs (cervical osteochondrosis), chest painwhich mimics an angina or heart attack, intercostal neuralgia (thoracic osteochondrosis), cauda equina syndrome, numbness of the lower limbs (lumbar-sacral osteochondrosis).
On a note. Pathology causes vegetovascular and neurodystrophic disorders.
Diagnostic
To establish an accurate diagnosis, the patient is sent for X-ray, myelography and neurological examination of reflexes. If this is not enough, a referral is issued to:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- CT (computed tomography);
- NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance).
The doctor also interviews the patient and performs a medical examination that reveals areas of pain, possible curvature of the spine, discrepancy in leg lengths, and other objective signs of spinal injury.
Therapy
The treatment of osteochondrosis is complex. To stop the process of degeneration, or at least slow it down, are assigned:
- chondroprotectors - externally, orally (by mouth), injections to restore cartilage tissue;
- muscle relaxants - relax spasmodic muscle groups, are used only under medical supervision;
- painkillers;
- blockages - relieve pain for a long time, but do not heal;
- physiotherapy (magnetotherapy, phonophoresis, vibrotherapy, EHF and others);
- exercise therapy and author's gymnastics;
- massage;
- acupuncture;
- balneotherapy and mud therapy.
In advanced cases (uncontrolled urination and defecation, cauda equina syndrome), surgery may be required to decompress and stabilize the affected spinal segments.
Decompression operations with posterior access:
- facetectomy;
- foraminotomy;
- laminectomy;
- laminotomy.
Decompression operations with prior access:
- discectomy;
- corpectomy.
To stabilize the damaged segment, spinal fusion is used - the fusion of adjacent vertebrae using a special fixed structure (rods). A bone implant is placed in place of the removed intervertebral disc (the bone material is either taken from a donor or formed from the patient's own bone).
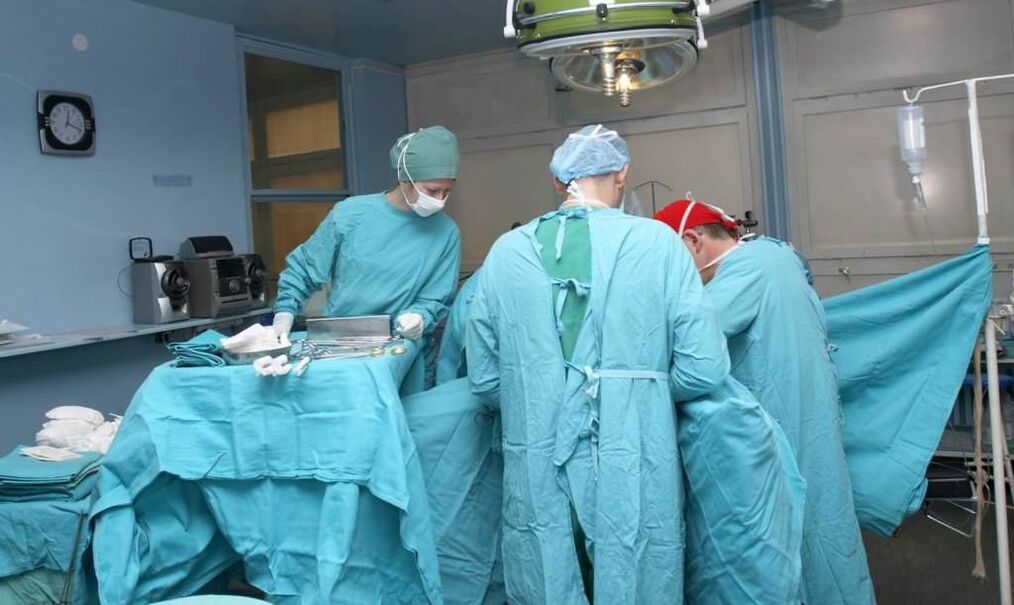
On a note. Spinal fusion can be avoided. Surgeons have done a lot in the surgical treatment of osteochondrosis. Instead of a removed intervertebral disc, it is possible to install an artificial one and thus avoid complete immobilization of the segment. Operations on the spine are fraught with many complications, so they are prescribed only in extreme cases.
Prevention
Even Hippocrates said, "It is easier to prevent disease than to cure it. This rule also applies to osteochondrosis. It is enough for a person to monitor his health, lead an active lifestyle, eat right, exercise regularly to maintain the health of the spine.

If the disease nevertheless manifested itself, prevention will help not to trigger it. Follow these guidelines:
- Sleep on the right mattress and pillow. Choose orthopedics and consult your doctor first.
- Make it a rule to walk at least half an hour before and after work. During the break, do not sit in front of the computer or on the phone, but warm up, then have a snack.
- Watch your weight. The higher it is, the harder it is on the spine.
- Observe rest mode (work during the day, sleep at night).
- Try to eliminate stress from your life. If you feel that you are falling into depression, consult a specialist.
On a note. Traditional healers claim that osteochondrosis can be cured with the help of medicinal herbs. It is difficult to say how true this statement is. Treatment with alternative methods can be used along with that prescribed by the doctor. Otherwise, the result is not guaranteed.
Osteochondrosis is a dangerous disease, fraught with disability if treatment is not started in time. If you feel that you are tired quickly, and in the morning the spine is less flexible than before, consult a doctor and undergo a complete examination. In the early stages, the pathology can be slowed down and even completely stopped.